With the push towards carbon neutrality growing, and as a worrying trend of rising temperatures and natural disasters caused by global warming continues, solar cells will play a pivotal role in the world’s transition to renewable energy.
Now, a research group has laid the path for achieving higher open-circuit voltage in tin sulfide (SnS) solar cells, thus realizing their latent potential as a thin-film solar material.
Thin-film solar cells, which comprise compound semiconductors with strong light absorption, require less raw materials, making them lighter and cheaper to produce.
SnS is one such thin-film solar cell material with environmentally friendly credentials, since it contains no rare or toxic elements. Yet, in recent years, researchers have begun to question this premise since, despite more than 20 years of research into them, their conversion efficiency had reached a mere 5% due to a low open-circuit voltage.
The group, which was led by Assistant Professor Issei Suzuki, from Tohoku University’s Institute of Multidisciplinary Research for Advanced Materials, successfully demonstrated a SnS interface exhibiting large band bending—something necessary for obtaining a higher open-circuit voltage.
“We used photoelectron spectroscopy to analyze the electronic structure of the interface where molybdenum oxide was deposited on a SnS single crystal,” said Suzuki. “We confirmed that the interface state achieved a high open-circuit voltage.
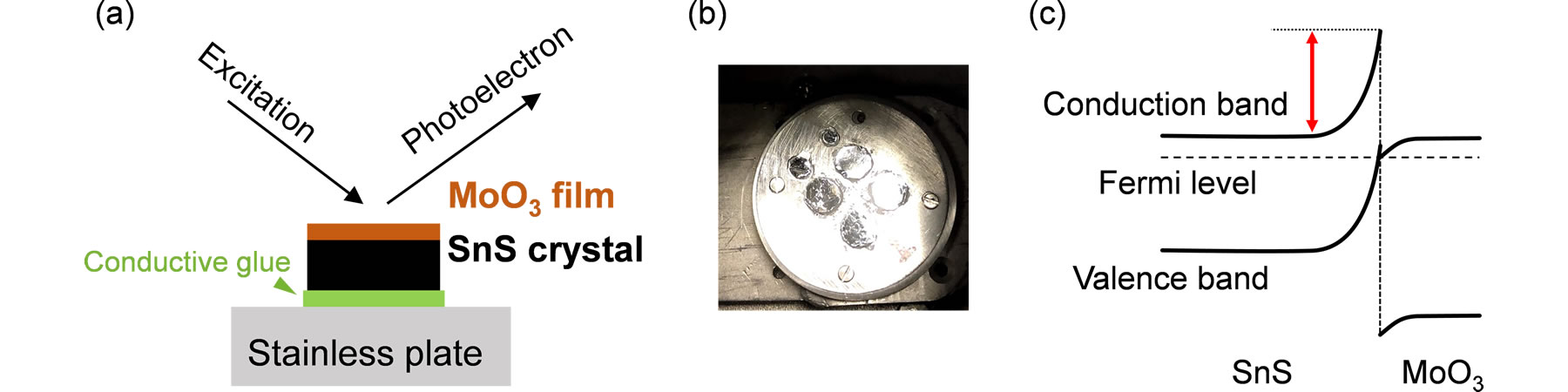 (a) Schematic of the interface between the SnS single crystal/MoO3 thin film analyzed in this study. (b) A sample actually used for the photoelectron spectroscopy measurement. Several single crystals are fixed on a stainless-steel plate. (c) Schematic energy band diagram of the present interface where SnS band exhibited large bending. ©Issei Suzuki et al. |
This is not Suzuki’s first breakthrough in SnS thin-film solar cells either. Back in December 2021, he led another group that produced the world’s first n-type SnS thin film. This enabled homojunctions to be formed in thin films.
For the current research, the group also proposed a method for fabricating interfaces suitable for SnS thin-film solar cells, including reducing the sulfur deficiency in the SnS thin films and employing a homojunction structure in their n-type and p-type layers.
 A conceptual image of the analysis performed in this study: SnS is proved to be a promising photovoltaic (PV) material. ©Issei Suzuki et al. |
“In the near future, we hope to fabricate homojunction solar cells with high conversion efficiency,”added Suzuki.
Details of the group’s research were published in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C.
For further information on the previous success in developing n-type SnS thin films, see here.
Publication Details
“Avoiding Fermi Level Pinning at the SnS Interface For High Open-Circuit Voltage”
Issei Suzuki, Binxiang Huang, Sakiko Kawanishi, Takahisa Omata, Andreas Klein
The Journal of Physical Chemistry C
DOI:10.1021/acs.jpcc.2c04212
▶ Information in Japanese
▶ Tohoku University
▶ Atomic Site Control in Inorganic Materials
▶ https://sites.google.com/view/isseis/issei-suzuki-tohoku-univ
Contact
Email:issei.suzuki[at]tohoku.ac.jp